Choosing the Right Rock Breaker for Mining Success
What Is a Rock Breaker?
A Rock Breaker serves as a powerful tool that excavator operators use to break rock and concrete. Operators mount the Rock Breaker on a carrier machine. They position the chisel tip directly against the rock. The carrier’s hydraulic system drives the piston to strike the rock with force. Operators use Rock Breakers in quarries, mines, and construction sites. Maintenance crews inspect and service the Rock Breaker regularly to keep it operational.
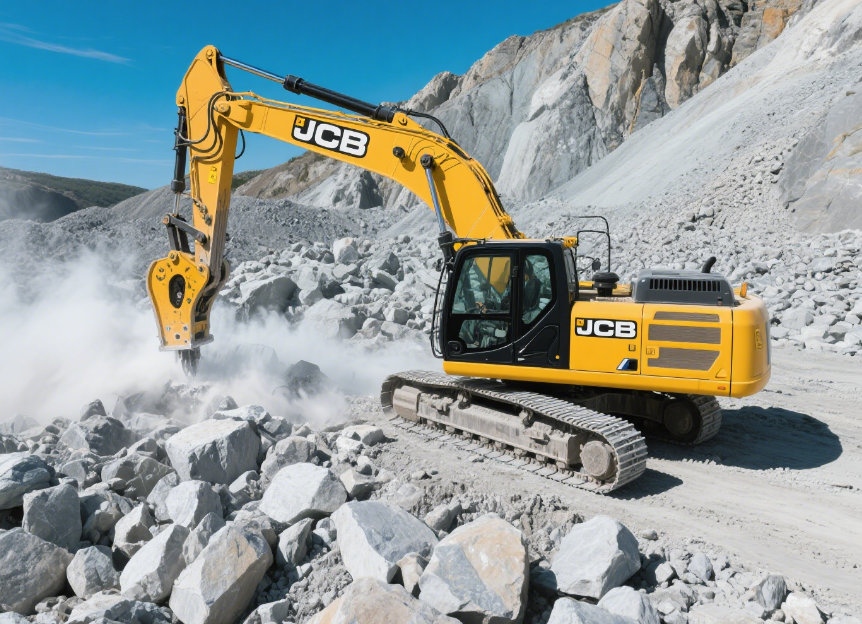

Why Do Operators Use a Mining Rock Breaker?
Operators choose a Mining Rock Breaker to quickly reduce rock size and lower labor costs. They break oversized rocks that crushers cannot handle. Operators use the Mining Rock Breaker to pre-fracture rock before blasting. This action improves fragmentation and reduces the need for explosives. Engineers design mine layouts to include the Mining Rock Breaker for better efficiency. Procurement teams evaluate different Mining Rock Breaker models to meet production demands.
How Does Rock Breaker Operation Work?
The carrier pumps hydraulic oil into the Rock Breaker Operation chamber under high pressure. The piston moves forward and drives the chisel into the rock. The piston retracts and repeats this process rapidly. Operators adjust the blow frequency and impact energy to match the rock type. Maintenance teams check the hydraulic hoses, oil flow, and piston speed to ensure stable Rock Breaker Operation. Crews measure cycle times to verify that the Rock Breaker Operation meets productivity goals.
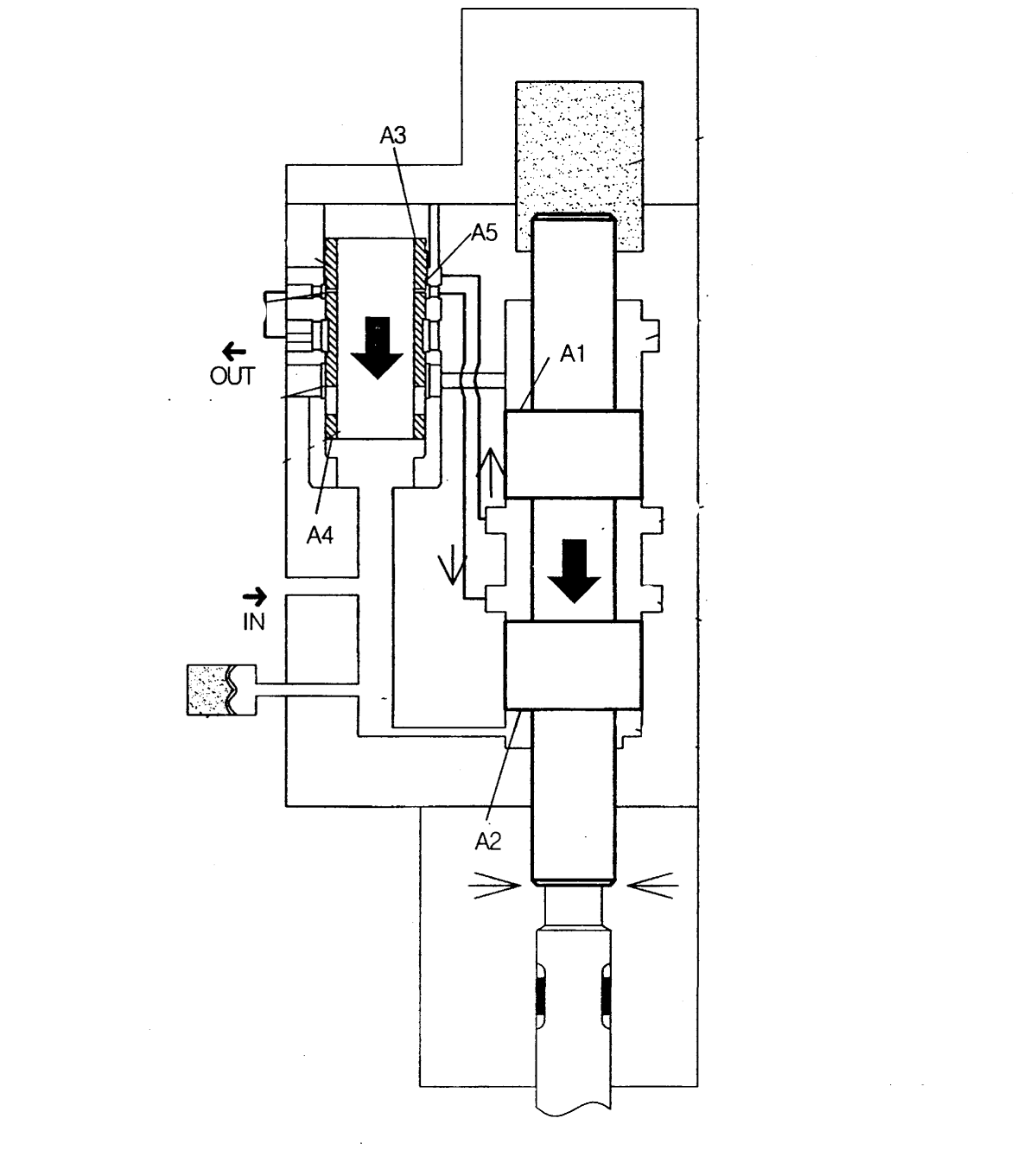
What Are the Benefits of Rock Breaker Performance?
Superior Rock Breaker Performance delivers clear benefits:
- Faster Cycle Times
Operators use high piston speed to deliver rapid blows and reduce operation time. - Precise Material Control
Operators adjust impact force to control breakage and protect nearby equipment. - Lower Maintenance Costs
Crews replace chisel bits quickly and complete Rock Breaker Performance checks efficiently. - Reduced Noise and Vibration
Designers add dampening systems to lower vibration and extend carrier life.
How to Select the Best Rock Breaker for Mining
Procurement teams follow these steps to select the Best Rock Breaker for Mining:
- Match Carrier Capacity
Teams compare the carrier’s hydraulic flow and pressure to the Best Rock Breaker for Mining specifications. - Evaluate Impact Energy
Teams review energy per blow and choose a tool that matches rock hardness. - Confirm Weight and Size
Teams select a size that fits the carrier and ensures safe handling. - Check Service Accessibility
Teams choose a model that allows fast chisel and seal replacement. - Calculate Total Cost of Ownership
Teams review purchase price, service costs, and expected lifespan to choose the Best Rock Breaker for Mining.
How to Compare Hydraulic Rock Breaker and Pneumatic Rock Breaker
Project teams compare the Hydraulic Rock Breaker and Pneumatic Rock Breaker using these points:
- Power Source
The Hydraulic Rock Breaker uses the carrier’s hydraulic pump. The Pneumatic Rock Breaker connects to an air compressor. - Blow Rate
The Hydraulic Rock Breaker produces slower but more powerful blows. The Pneumatic Rock Breaker delivers faster, lighter blows. - Mobility
Operators move the Hydraulic Rock Breaker easily with the carrier. The Pneumatic Rock Breaker requires hose connections and compressor transport. - Service Needs
Crews service hydraulic parts on the Hydraulic Rock Breaker and inspect air filters on the Pneumatic Rock Breaker. - Job Cost
Teams avoid compressor rental fees when they use the Hydraulic Rock Breaker. The Pneumatic Rock Breaker often fits small projects with existing air setups.
How to Complete Rock Breaker Maintenance
Field crews complete Rock Breaker Maintenance by following these tasks:
- Perform Daily Visual Checks
Crews inspect pins, hoses, and fasteners every day. They tighten any loose parts immediately. - Apply Regular Grease
Crews grease all lubrication points before and after shifts to reduce wear. - Check Hydraulic Oil
Technicians sample the hydraulic oil and check for contamination. - Replace Chisel Bits
Crews replace worn chisels as soon as they see damage. - Change Seal Kits
Maintenance teams replace internal seals on schedule to prevent leaks.
How to Enforce Rock Breaker Safety
Supervisors enforce strict Rock Breaker Safety procedures:
- Set Up Clear Zones
Crews place barriers and warning signs around the work area. - Use Protective Gear
Operators wear helmets, face shields, ear protection, and steel-toe boots. - Inspect Before Use
Supervisors inspect pins, hoses, and guards before every shift. - Control Work Zones
Crews maintain a 10-meter exclusion zone around the active Rock Breaker Safety area. - Stay Ready to Stop
Operators keep their hands near the emergency shutoff valve.
How to Follow the Rock Breaker Selection Guide
Project teams follow the Rock Breaker Selection Guide step by step:
- Measure Rock Hardness
Teams test samples to confirm the rock’s strength. - Calculate Impact Requirements
Engineers compute the required energy based on rock properties. - Confirm Carrier Match
Teams verify the carrier’s hydraulic capacity matches the selected breaker. - Review Site Conditions
Teams check temperature, dust, and noise levels to choose proper seals and cooling options. - Compare Models
Teams collect data from suppliers and select top models using the Rock Breaker Selection Guide.
How to Troubleshoot Rock Breaker Operation
Service teams troubleshoot Rock Breaker Operation using clear steps:
- Solve Weak Impact Force
Technicians increase hydraulic flow and replace worn chisels to restore power. - Stop Hydraulic Overheat
Teams clean the oil cooler and schedule work breaks to lower temperatures. - Fix Oil Leaks
Technicians replace damaged seals and hoses quickly. - Improve Slow Cycle Time
Teams flush contaminated hydraulic oil and rebuild valves to restore speed. - Reduce Vibration
Crews tighten loose pins and replace worn bushings to stabilize the tool.
Summary of Key Takeaways
Operators rely on a Rock Breaker to improve mining efficiency. The Mining Rock Breaker reduces oversized rocks and speeds up material handling. The Rock Breaker Operation depends on strong hydraulic power and proper settings. Teams achieve strong Rock Breaker Performance when they follow proper procedures. Procurement teams select the Best Rock Breaker for Mining by matching tool size, carrier capacity, and service needs. Teams compare Hydraulic Rock Breaker and Pneumatic Rock Breaker carefully to fit site conditions. Field crews complete daily Rock Breaker Maintenance to prevent failures. Supervisors enforce strict Rock Breaker Safety to protect workers. Teams use the Rock Breaker Selection Guide to choose the right tool and troubleshoot problems quickly. Companies that follow these steps improve productivity and save costs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How can I match a carrier to the Best Rock Breaker for Mining?
You can compare the carrier’s hydraulic flow and pressure with the breaker’s requirements. You must ensure that the carrier matches the Best Rock Breaker for Mining specifications.
Q2: How often should I perform Rock Breaker Maintenance?
You should perform daily inspections and greasing. You should replace seals every 500 hours. This schedule keeps the Rock Breaker Maintenance on track.
Q3: What protective equipment supports Rock Breaker Safety?
Operators must wear helmets, ear protection, face shields, and steel-toe boots. Supervisors must enforce Rock Breaker Safety rules at all times.
Q4: When should I choose a Pneumatic Rock Breaker instead of a Hydraulic Rock Breaker?
You should choose a Pneumatic Rock Breaker if your site uses an air compressor system. You should select a Hydraulic Breaker when you need high-impact energy powered by the excavator.